
When your window AC isn’t cutting it, but central AC is too expensive, installing a new ductless mini-split AC may be the cooling solution you’re looking for. Find out what a mini-split costs and how to hire the right pros to get the job done.


Furnace sizes are expressed in BTUs, which measure the amount of heat created per hour. Most furnaces range from 30,000 to 120,000 BTUs.
You can determine the size furnace you need based on your home’s square footage.
Other factors in calculating the size include the efficiency of your windows and doors, the climate you live in, and how well insulated the home is.
Gas furnace costs range from as low as $500 to as high as $6,000 or more depending on the size and efficiency.
It may pay to hire a pro to assess your home to determine the proper furnace size.
Calculating what size furnace you need will help you heat your home as efficiently as possible. Generally speaking, the furnace size depends on the square footage of your home, but you should also factor in other criteria such as the efficiency of your windows, doors, and insulation as well as the efficiency of the furnace itself. Use these calculations to figure out what size furnace you need.
Using the table below, you can use the size of your home to determine the right size furnace based on its British Thermal Units (BTUs).
| Home Size (in Square Feet) | Furnace Size (in BTUs) |
|---|---|
| 750–1,000 | 22,500–60,000 |
| 1,000–1,250 | 30,000–75,000 |
| 1,250–1,500 | 37,500–90,000 |
| 1,500–1,750 | 45,000–105,000 |
| 1,750–2,000 | 52,500–120,000 |
| 2,000–2,500 | 60,000–150,000 |
| 2,500–3,000 | 75,000–180,000 |
The calculation for how big a furnace needs to be is based on 30 to 60 BTUs per square foot. So if your home is 1,000 square feet, you’ll need a furnace that provides between 30,000 and 60,000 BTUs. You can use the following formulas to roughly calculate what size furnace you need for your home.
Furnace Size for a Milder Climate = Home’s Square Footage x 30
Furnace Size for a Colder Climate = Home’s Square Footage x 60
The actual number of BTUs your furnace will need will depend on your climate as well as factors like whether or not you have a well-insulated home, the home’s age, window and door quality, and furnace efficiency.
Here’s how to take the most accurate measurements to decide what size furnace to get.
To calculate the right size furnace for your home, you should start with the size of the home itself. There are other factors to consider as well, but we’ll start with calculating your home’s square footage. You do this by measuring the length and width of each room and multiplying those two numbers together.
Room Length (in feet) x Room Width (in feet) = Room’s Square Footage
You may need to break the room into smaller sections if the room is an irregular shape and then add the smaller areas together.
After you’ve measured each room, add all of the room areas together to get the total amount of square footage in your home.
Once you have the square footage measurement, you can determine the furnace BTU range. Once you have that, you can use the chart in the next section to narrow down the furnace size you need.
In addition to accounting for the home’s square footage, furnace size calculations will also depend on your climate zone. Using the following climate graphic and climate zone chart, determine what climate zone you're in and how many BTUs are recommended per square foot.
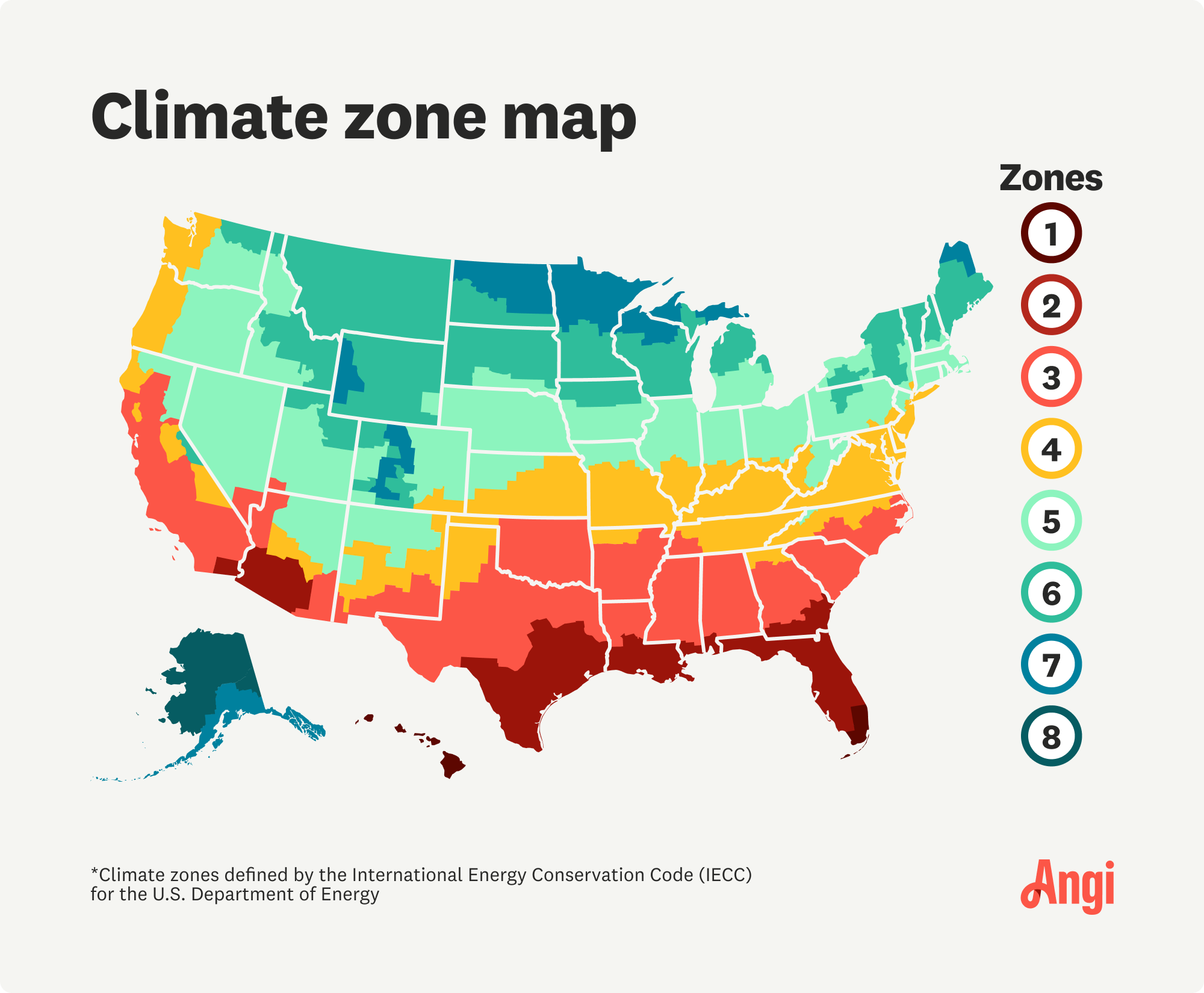
| Climate Zone | BTUs per Square Foot |
|---|---|
| 1 | 30–35 |
| 2 | 35–40 |
| 3 | 40–45 |
| 4 | 45–55 |
| 5 | 55–70 |
| 6 | 70–80 |
| 7 | 80–90 |
| 8 | 90–100 |
You can get an initial idea of the proper furnace size by calculating your home’s square footage, but to get the most accurate measurement, you should reach out to a local furnace installer. They’ll be able to determine the quality of your insulation and doors, and they’ll take other factors like furnace efficiency, high-efficiency windows, and climate into account to make the best recommendation.
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

When your window AC isn’t cutting it, but central AC is too expensive, installing a new ductless mini-split AC may be the cooling solution you’re looking for. Find out what a mini-split costs and how to hire the right pros to get the job done.

Discover the factors influencing air duct replacement costs in Atlanta, GA. Learn how to save money and make an informed decision for your home's comfort.

What you’ll pay in Atlanta, Georgia, for furnace repairs depends on many factors. Here’s a breakdown of what can go wrong and the cost to fix those issues.

Tackling unwanted odors from indoor plants can be tricky. Learn how to use a carbon filter in your duct fan to improve air quality.

Discover the average air handler replacement cost, including labor and materials, plus expert tips to help you budget and save on your HVAC upgrade.

You’ll need to get creative if you want to run your portable AC in a windowless room. Here’s how to vent a portable air conditioner without a window.